In today’s digital age, cybersecurity tips for small business owners are more critical than ever. Small businesses, often overlooked by cybercriminals, are prime targets due to their limited resources and less robust security systems. According to a recent report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2023 was $4.45 million, and small businesses face a 43% higher chance of experiencing a cyberattack compared to larger enterprises. This article provides cybersecurity tips for small business owners to safeguard their operations, protect sensitive data, and maintain customer trust in an increasingly connected world. From password security to data backup strategies, we’ll explore actionable steps to build a resilient cybersecurity foundation that stands the test of time.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding Cybersecurity Risks for Small Businesses
Cybersecurity threats are not limited to large corporations; they affect small businesses in alarming numbers. Whether it’s phishing scams, ransomware attacks, or malware infections, the risks are diverse and constantly evolving. Small business owners often underestimate these dangers, assuming that they are too small to be targeted. However, the reality is that cybercriminals target businesses of all sizes, often exploiting weak defenses to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.
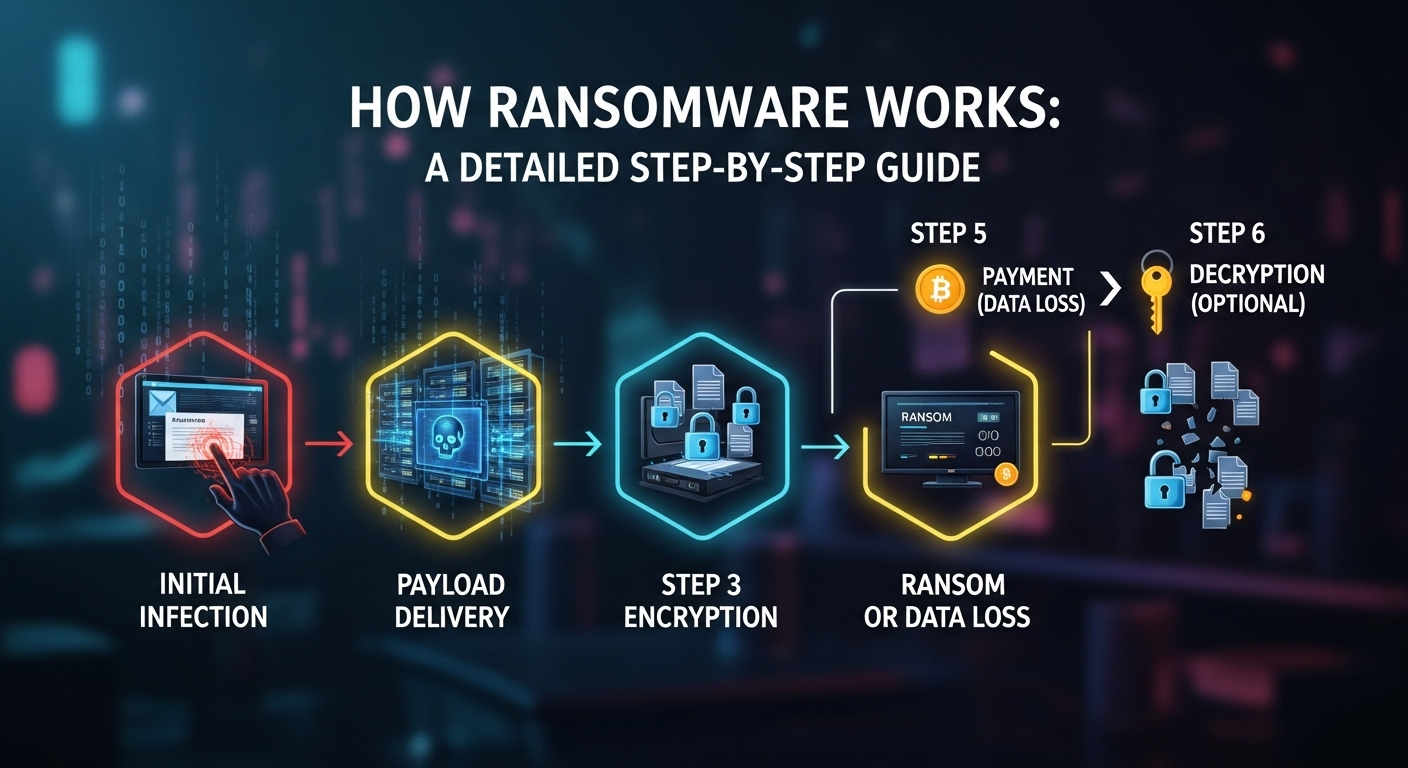
One of the most common risks is data breaches, which can result in the exposure of customer data, financial records, and intellectual property. These breaches not only lead to financial losses but also damage a business’s reputation and customer relationships. Another significant threat is ransomware, where attackers encrypt a business’s files and demand payment in exchange for the decryption key. This type of attack can cripple operations, especially if the business relies heavily on digital systems.
Common Cyber Threats and Their Impact
Small businesses face a wide range of cyber threats, including phishing attacks, malware infections, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Phishing is particularly effective because it relies on social engineering to trick employees into revealing login credentials or financial information. Malware, such as viruses or spyware, can infiltrate systems through infected emails, USB drives, or malicious websites. Meanwhile, unsecured Wi-Fi networks may leave sensitive data vulnerable to interception by hackers.
The impact of these threats can be devastating. A single data breach can lead to financial losses, legal penalties, and a loss of customer confidence. For instance, a 2022 study by the Ponemon Institute found that 60% of small businesses that experienced a cyberattack went out of business within six months. This highlights the importance of proactive measures to mitigate risks.
The Cost of Cybersecurity Negligence
Ignoring cybersecurity tips for small business owners can result in significant financial consequences. Beyond the direct costs of breaches, businesses may incur recovery expenses, loss of productivity, and potential fines for regulatory violations. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes hefty fines on companies that fail to protect personal data, up to 4% of annual global revenue.
Moreover, the indirect costs of cyberattacks are often overlooked. These include the cost of reputational damage, increased insurance premiums, and operational downtime. A small business with a strong online presence may lose customers if they fail to secure their website or protect client data. By understanding these potential costs, owners can prioritize cybersecurity as a vital part of their business strategy.
The Role of Human Error in Cybersecurity
Even the most advanced security systems can be compromised by human error. Employees are often the weakest link in a business’s cybersecurity defenses, as they may click on suspicious links, use weak passwords, or fall victim to social engineering tactics. A 2023 survey by Verizon revealed that 85% of data breaches involved human error, emphasizing the need for ongoing employee training and awareness.
Small business owners should recognize that cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. Training employees to recognize phishing attempts, follow secure practices, and report suspicious activity can significantly reduce the risk of breaches. Investing in regular cybersecurity training sessions ensures that staff stay updated on the latest threats and countermeasures, creating a culture of security within the organization.
Implementing Basic Cybersecurity Measures
To protect their business, small business owners should start with fundamental cybersecurity tips for small business owners. These include strong password policies, data encryption, and regular software updates. While these measures may seem simple, they form the backbone of a secure digital environment.
Creating Strong Passwords and Using Multi-Factor Authentication
A strong password is the first line of defense against unauthorized access. Weak passwords are easy targets for hackers, who can use brute-force attacks to guess them. Small businesses should enforce password policies that require complex passwords, regular changes, and avoid reusing the same password across multiple accounts.
In addition to strong passwords, multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security. MFA requires users to provide two or more verification methods, such as a password and a one-time code sent to their phone. According to Microsoft, MFA can block over 99% of automated attacks on accounts. Small business owners should enable MFA for all critical accounts, especially those handling financial transactions or customer data.
Securing Data with Encryption
Data encryption is a powerful tool to protect sensitive information from being accessed by unauthorized parties. Whether it’s customer data, employee records, or business financials, encrypted data remains secure even if it’s intercepted. Small businesses should use encryption for data at rest (stored data) and data in transit (data being transferred over the internet).
For example, SSL/TLS encryption ensures that online transactions are secure, while full disk encryption protects data stored on computers or servers. Implementing encryption reduces the risk of data exposure, especially in the event of a breach or ransomware attack. Small business owners should also consider encrypting backups to ensure that even if the primary data is compromised, the backups remain safe.
Regular Software and System Updates
Outdated software and systems are vulnerable to exploits that cybercriminals can use to infiltrate networks. Regular updates ensure that known security flaws are patched, reducing the risk of attacks. Small business owners should establish a schedule for updating operating systems, applications, and firmware.
Automated updates can simplify this process, but it’s essential to manually check for critical patches as well. For instance, Microsoft Windows and Linux distributions often release security updates that address zero-day vulnerabilities. By keeping software up to date, businesses can protect themselves from exploits that are already known to attackers.
Employee Training and Awareness
Human error is one of the leading causes of cybersecurity breaches, making employee training a crucial component of any business’s security strategy. Small business owners should invest in regular training sessions to educate their staff on common threats and safe digital practices. This ensures that employees are prepared to identify and respond to potential risks.
Phishing Awareness and Social Engineering Defense
Phishing attacks are a favorite method of cybercriminals, as they rely on social engineering to trick employees into revealing login credentials or sensitive information. Cybersecurity tips for small business owners include conducting phishing simulations to train employees to recognize suspicious emails. These simulations can help identify weak points in an employee’s vigilance and improve overall security posture.
For instance, a phishing email that mimics a trusted source, such as a bank or a customer, can be designed to look legitimate. Employees should be taught to verify the sender’s email address, check for typographical errors, and avoid clicking on unknown links or attachments. By fostering a culture of awareness, small businesses can significantly reduce the likelihood of falling victim to these attacks.
Securing Company Devices and Networks
Small businesses often use personal devices for work, which can introduce security risks if not properly managed. Cybersecurity tips for small business owners should include implementing device security policies that require password protection, screen locks, and data encryption on all devices. This ensures that even if a device is lost or stolen, the data remains secure.
Additionally, securing Wi-Fi networks is essential. Business owners should use strong passwords and WPA3 encryption to prevent unauthorized access. They should also disable unnecessary features on routers, such as remote administration, to reduce potential entry points for attackers. By training employees to use secure networks and protect their devices, small businesses can minimize the risk of internal breaches.
Protecting Business Data with Backups and Cloud Security
Data loss can be catastrophic for any business, but it is particularly damaging for small businesses that may not have the resources to recover quickly. Cybersecurity tips for small business owners should emphasize the importance of data backups and cloud security measures. These steps ensure that critical information is preserved in case of a cyberattack, hardware failure, or natural disaster.
Creating a Robust Backup Strategy
A reliable backup strategy is essential for data recovery. Small businesses should store backups offline or in secure cloud storage to protect against ransomware attacks, which often target online data. Regular backups should be performed automatically, and multiple copies should be stored in different locations to ensure redundancy.

For example, a 3-2-1 backup rule recommends keeping three copies of data, storing two on different media, and having one offsite. This approach minimizes the risk of total data loss. Additionally, backup verification should be conducted periodically to ensure that data can be restored when needed. By following these best practices, small businesses can protect their data and avoid disaster recovery costs.
Choosing Secure Cloud Storage Solutions
Cloud storage offers convenience and scalability, but it also requires proper security measures. Small business owners should select cloud providers with strong encryption protocols, regular security audits, and data breach response plans. Popular cloud services like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 provide advanced security features, including two-factor authentication and role-based access control.
However, even with secure cloud storage, data breaches can occur if access controls are not properly managed. Businesses should limit user permissions to only essential data, monitor access logs, and enable encryption for data in transit and at rest. By implementing these cloud security practices, small businesses can reduce the risk of data exposure while maintaining efficient data management.
Monitoring and Responding to Cybersecurity Threats
Proactive monitoring and quick response strategies are vital for cybersecurity tips for small business owners. Cyber threats are constantly evolving, so continuous monitoring helps identify potential vulnerabilities and prevents attacks before they cause significant damage.
Utilizing Cybersecurity Tools and Services
Small businesses can benefit from cybersecurity tools such as firewalls, antivirus software, and intrusion detection systems. These tools act as digital sentinels, monitoring network traffic and identifying suspicious activity. For instance, a firewall can block unauthorized access to the business’s network, while antivirus software detects and removes malware.
Additionally, managed security services can provide expert support for businesses that lack in-house cybersecurity resources. These services offer real-time monitoring, threat intelligence, and incident response capabilities. By outsourcing cybersecurity tasks, small business owners can focus on their core operations while ensuring their digital assets are secure and protected.
Establishing an Incident Response Plan
An incident response plan is a crucial component of cybersecurity preparedness. It outlines steps to take in the event of a data breach or cyberattack, ensuring a swift and effective response. Small business owners should document procedures, designate roles, and test the plan regularly to identify gaps and improve response times.
For example, in the case of a ransomware attack, the response plan may include isolating infected systems, notifying stakeholders, and restoring data from backups. This structured approach minimizes downtime and reduces the impact of the attack. By having a clear response plan, businesses can rebound faster and protect their reputation.
Cybersecurity Best Practices for Long-Term Protection
To ensure long-term cybersecurity protection, small business owners should adopt best practices that address both current and future threats. These practices include implementing firewalls, updating security protocols, and conducting regular audits. By taking a proactive approach, businesses can stay ahead of cybercriminals and minimize risks.
Deploying Firewalls and Network Security
A firewall is a digital barrier that blocks unauthorized access to a business’s network. Small businesses should install and configure firewalls to monitor incoming and outgoing traffic, filter malicious activity, and protect sensitive data. Additionally, network segmentation can be used to isolate critical systems, reducing the risk of widespread breaches.
For example, firewalls can block traffic from suspicious IP addresses, while network segmentation ensures that a compromised device does not access the entire network. Small business owners should also regularly update firewall rules and monitor logs for unusual patterns. By securing the network, they can prevent attackers from gaining a foothold in their systems.
Regular Cybersecurity Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting regular cybersecurity audits helps identify vulnerabilities and assess security effectiveness. These audits can be internal or external, with external audits often providing fresh perspectives and compliance checks. Small business owners should schedule audits at least once a year or quarterly for high-risk operations.
Penetration testing, or ethical hacking, involves simulating cyberattacks to test system defenses. This hands-on approach reveals weak points that may be exploited by real attackers. For instance, a penetration test could expose a weak password policy or unpatched software. By addressing these issues, businesses can strengthen their security posture and avoid costly breaches.
FAQ: Common Questions About Small Business Cybersecurity
Q1: What are the most common cyber threats small businesses face?
Small businesses are frequently targeted by phishing attacks, malware, ransomware, and unsecured Wi-Fi networks. Phishing remains the leading cause of breaches, as it exploits human error to gain access to sensitive information. Malware can infiltrate systems through email attachments or downloaded software, while ransomware encrypts data and demands payment. Unsecured Wi-Fi can be a gateway for hackers to access company networks.
Q2: How can I protect my business from ransomware?
To protect against ransomware, small businesses should implement regular data backups, use strong passwords, and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA). Staying updated with software patches is also critical, as unpatched systems are more susceptible to exploits. Additionally, training employees to recognize phishing emails reduces the risk of initial ransomware infection.
Q3: Why is employee training important in cybersecurity?
Employee training is vital because human error accounts for a majority of breaches. Employees who are aware of cybersecurity risks are less likely to click on phishing links, download malicious files, or share sensitive data with unauthorized parties. Training also fosters a culture of security, ensuring that all staff members play a role in protecting the business.
Q4: How often should I update my software and systems?
Small business owners should update software and systems regularly, ideally weekly or monthly, depending on the risk level. Critical updates, especially those addressing security vulnerabilities, should be applied immediately. Automating updates where possible reduces the risk of human oversight, while manual checks ensure that all components are secure.
Q5: What should I do in case of a data breach?
In the event of a data breach, small businesses should notify affected customers and regulatory authorities promptly. Contain the breach by isolating infected systems, investigating the cause, and restoring data from backups. Review security measures to prevent future breaches, and document the incident for compliance and improvement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity tips for small business owners are essential for protecting digital assets and ensuring business continuity. By understanding common threats, implementing strong security measures, and training employees, small businesses can minimize risks and build resilience. The use of encryption, regular backups, and proactive monitoring further enhance security posture. As cyber threats evolve, small business owners must remain vigilant, adapt their strategies, and prioritize cybersecurity as a core business function.
Table: Cybersecurity Statistics for Small Businesses
| Threat Type | Average Cost (2023) | Common Vulnerabilities | Prevention Tips | |————————–|————————–|———————————————–|————————————————| | Phishing Attacks | $4.45 million | Weak passwords, lack of training | Implement MFA, conduct phishing simulations | | Ransomware Attacks | $5.42 million | Unpatched software, insecure networks | Regular updates, network segmentation | | Data Breaches | $4.45 million | Exposed customer data, insider threats | Encryption, access control, incident response | | Malware Infections | $1.95 million | Outdated software, unsecured devices | Automatic updates, device encryption | | Social Engineering | $2.13 million | Trust in phishing emails, leaked credentials | Employee awareness training, verification |
By following these cybersecurity tips for small business owners, you can safeguard your business from potential threats and build a secure digital environment.
Summary: This article provides essential cybersecurity tips for small business owners to protect their operations from increasing cyber threats. Key strategies include implementing strong password policies, securing data with encryption, and regular software updates. Employee training is crucial for minimizing human error, while data backups and cloud security ensure recovery readiness. A comprehensive incident response plan and continuous monitoring further strengthen security posture. By adopting these best practices, small businesses can reduce risks, maintain customer trust, and navigate the digital landscape safely.