Discover the benefits, challenges, and future of blockchain technology, a revolutionary system enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency in various industries.
Blockchain technology has transformed from a cryptocurrency backbone into a wide-reaching, transformative innovation influencing diverse sectors.
From supply chain management to secure voting systems, blockchain offers solutions for transparency, security, and trust.
Let’s dive into blockchain’s core principles, advantages, real-world applications, challenges, and its bright future in reshaping the digital world.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized, distributed ledger that stores transactional data across a network of computers.
Unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority, blockchain’s unique structure ensures data is secure, transparent, and nearly immutable. Here, we’ll explore the essential components that define blockchain.
Key Concepts of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain operates on principles like decentralization, transparency, and cryptographic security. Below, we delve into these foundational elements that make blockchain both powerful and disruptive.
Decentralization
Traditional databases often rely on a central authority to control and manage information. Blockchain, however, operates on a peer-to-peer network, spreading data across multiple nodes globally. This decentralized nature enhances security and reduces the risk of data manipulation by malicious actors.
Blocks and Chains
Data in blockchain is stored in blocks that are cryptographically linked in a chronological chain. Each block contains a unique code, or hash, connecting it to the previous block, ensuring data integrity. Changing any part of the blockchain requires altering every subsequent block, making tampering nearly impossible.
Consensus Mechanisms
To validate transactions, blockchain uses various consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). These protocols ensure data accuracy and prevent malicious actions.
PoW, for instance, requires significant computational work, while PoS prioritizes validators based on the number of tokens held, contributing to network security.
Transparency and Immutability
Blockchain’s transparency allows all participants to view the same data while ensuring it’s secure. Once data is recorded, it’s virtually unalterable, reinforcing trust and reliability among users.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when specific conditions are met, minimizing the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts have found applications in industries ranging from finance to healthcare.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
The advantages of blockchain extend beyond cryptocurrency, offering substantial improvements in security, cost efficiency, and transparency across sectors.
Enhanced Security
With data stored across numerous nodes and encrypted, blockchain is highly resistant to hacking. This makes it an attractive option for industries handling sensitive information, such as finance and healthcare.
Increased Transparency
All participants in a blockchain network access the same information, promoting trust and accountability. This transparency is especially beneficial in supply chains, where tracing a product’s journey is crucial.
Cost Reduction
Blockchain minimizes the need for intermediaries by enabling direct transactions. This reduction in third-party involvement can lead to significant cost savings, particularly in banking and real estate sectors.
Improved Traceability
Blockchain’s immutable ledger allows users to track every transaction step-by-step, which is invaluable in industries like logistics and pharmaceuticals. The ability to trace a product from its origin to the final customer enhances transparency and reduces fraud.
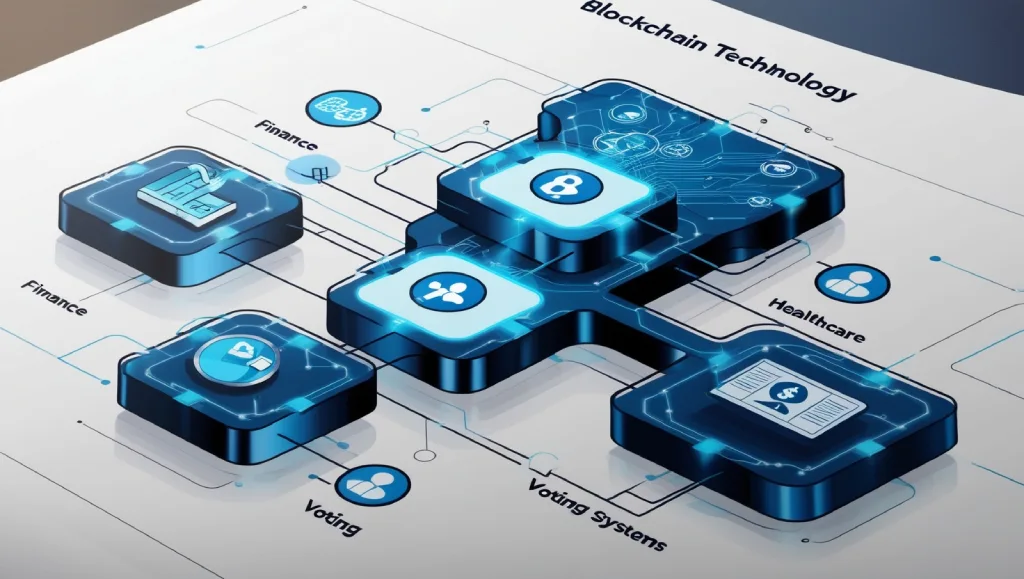
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has moved beyond financial transactions, finding relevance in various sectors. Here’s a look at the diverse applications where blockchain is making a difference.
Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum are the most well-known applications of blockchain. By utilizing a decentralized ledger, these digital currencies offer an alternative to traditional financial systems, facilitating quick, secure transactions across borders.
Supply Chain Management
In supply chains, blockchain enhances transparency and efficiency. It allows businesses to track products from manufacturing to delivery, reducing delays and errors. Companies can now ensure authenticity and quality at every stage.
Healthcare
Blockchain can securely store and share patient records, allowing healthcare providers access to critical information while maintaining privacy. This reduces the risk of data breaches and enables secure data sharing between healthcare providers.
Financial Services
Blockchain facilitates faster and more secure cross-border transactions, making it ideal for international trade and finance. By reducing reliance on intermediaries, blockchain streamlines transactions, reducing costs and delays.
Voting Systems
Blockchain’s transparency and security make it a promising solution for digital voting systems. A blockchain-based voting system could prevent tampering and ensure each vote is counted accurately, fostering trust in election results.
Challenges of Blockchain Technology
Despite its benefits, blockchain faces hurdles that must be addressed before achieving mainstream adoption.
Scalability
Blockchain networks like Bitcoin struggle to handle large transaction volumes quickly. Solutions like Layer 2 scaling (e.g., Lightning Network) are being explored, but scalability remains a critical issue for widespread adoption.
Energy Consumption
Proof of Work, the consensus mechanism used in Bitcoin, is computationally intensive and consumes significant energy.
Efforts to develop more energy-efficient consensus methods, such as Proof of Stake, are ongoing to address environmental concerns.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Blockchain’s global nature poses challenges for regulation. Different countries have varying approaches, creating a fragmented regulatory environment that complicates blockchain’s growth in sectors like finance.
Interoperability
Different blockchain networks operate independently, making cross-chain transactions difficult. Innovations like cross-chain bridges aim to improve interoperability, enabling different blockchains to communicate and work together.
User Awareness and Adoption
Many people still don’t fully understand blockchain or its potential benefits, which slows down its adoption. Educating the public and addressing misconceptions are essential for blockchain’s future growth.
Future of Blockchain Technology
As blockchain continues to evolve, new opportunities emerge in areas like Decentralized Finance (DeFi), Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), and more.
The potential for integration with AI and IoT offers exciting possibilities for creating more efficient, automated systems. The future of blockchain looks promising, with advancements expected in scalability, security, and energy efficiency.
FAQs on Blockchain Technology
- What is blockchain technology used for?
Blockchain is used for secure transactions, supply chain management, digital identity, and more. - Why is blockchain secure?
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature makes data tampering extremely difficult. - Can blockchain be hacked?
While highly secure, blockchain isn’t entirely hack-proof. However, hacking requires immense computational power and resources. - How does blockchain impact supply chains?
Blockchain enhances supply chain transparency, allowing companies to trace products and verify authenticity. - What is the future of blockchain?
Blockchain’s future includes integration with DeFi, AI, IoT, and potential applications in various industries.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is reshaping the digital landscape with its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature. From cryptocurrencies to healthcare and beyond, blockchain offers solutions that enhance efficiency and trust.
However, challenges remain, particularly around scalability and regulation. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to revolutionize industries, creating a more transparent, decentralized world.
For further insights and to stay updated on blockchain advancements, visit vpnpieces.com, your trusted source for information.















